背景
多目的ホール、駅構内、空港などの広い空間で音声が電気的に拡声される際、室内のスピーカから放射された音声には同時に長い残響が掛かることになる。このような残響環境下ではしばしば音声の聞きとりが低下するが、特に聴覚障害者・高齢者・非母語話者ではその影響は大きい。残響によって音声明瞭度が減少する原因として、先行音に付加された残響の尾が後続音をマスクする overlap-masking(Nabelek et al., 1989)があげられる。先行音が母音のようなエネルギの強い音素の場合、後続の音素は残響が付加された先行音による影響を大きく受けることが指摘されている(Arai et al., 2001, 2002)。図1の原音声と残響が付加された音声を比べると、音声波形の包絡が残響によってぼやけてしまっているのが分かる。
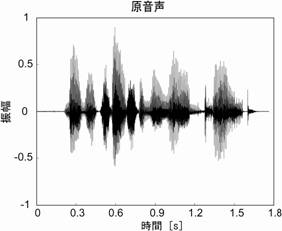
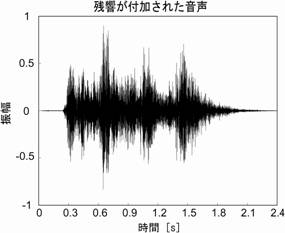
図1. 原音声 (左) と原音声に残響が付加された音声 (右)
手法
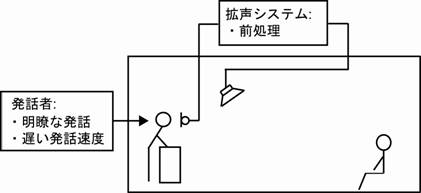
本研究の最終目標は、様々な人々が利用する公共空間においては、若年者だけではなく、聴覚障害者・高齢者・非母語話者に対しても聞きとりやすい音声を提供する、すなわち「音声のバリアフリー」を実現することである。私たちはこれまで、図2に示すように拡声システム側、発話者側の2方向からのアプローチで検討を行ってきた。拡声システム側からのアプローチでは、音声がスピーカから放射されるよりも前の段階で音声処理を行う「前処理」を提案している。前処理技術を用いると私たちは残響の影響を軽減する補聴機器を装着する必要がないことから、様々な人々が利用する公共空間では前処理は有効な明瞭度改善手法であると考えられる。
前処理側として私たちはこれまで、変調フィルタリングを用いた処理(例:Kusumoto et al., 1999, 2000, 2005)や、定常部抑圧処理(例:Arai et al., 2001, 2002; Hodoshima et al., 2006)を提案してきた。変調フィルタリングは、音声知覚に重要であるといわれている変調スペクトル(音声の時間変化に対するスペクトル)の低周波数領域(例:16Hz以下)(Houtgast and Steeneken, 1985)を強調する処理である。
定常部抑圧処理は、図3のように母音のようなエネルギの大きい音声の定常部を抑圧することでoverlap-masking を効果的に減少させる技術であるが、これは定常部の情報は遷移部の情報に比べて比較的冗長である(Furui, 1986)という点に着目しており、音声明瞭度を極力低下させずにoverlap-maskingの影響を軽減することができる。
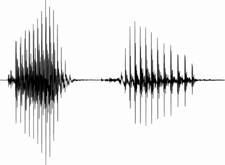
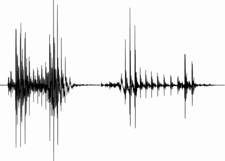
図3. 単語/aka/の原音声(左)と原音声に定常部抑圧処理を施した音声(右)
発話者側からのアプローチでは、残響にロバストな音声を調査している。音声明瞭度は話者によって変化するだけではなく、同一話者であっても話し方(例:はっきりした、会話調)や発話速度(例:ゆっくり、通常、速い)によっても変化する。私たちは残響下で明瞭な音声信号の特徴や、明瞭な発話・遅い発話速度の影響を調査している(例:Hodoshima et al., 2007)。
研究成果
残響環境と一口に言っても室環境などは公共空間によって様々であり、最適な明瞭度改善手法は公共空間によって異なるはずである。そこで私たちは、様々な受聴環境下で拡声システム側・発話者側の検討を行ってきた。
以下に主な研究成果を示す:
1) 拡声システム側
- 変調フィルタリングは残響下で若年健聴者の子音明瞭度を改善した (Kusumoto et al., 2005)。
- 重度の聴覚障害者は変調フィルタリング処理を行った音声の方が、処理をしていない音声よりも残響下で聞きやすいと判定した (Kusumoto et al., 1999, 2000)。
- 定常部抑圧処理は、次の条件において残響下で子音明瞭度を有意に改善した (例:Arai et al., 2007; Hodoshima et al., 2005, 2006, 2008a; Miyauchi et al., 2005; Nakata et al., 2006):
- 模擬残響環境下と講堂(残響時間0.7-1.3 s)
- 若年健聴者と高齢者
- 通常と遅い発話速度
2) 発話者側 (Hodoshima et al., 2007, 2008b)
- 残響下を想定して発話してもらった音声を若年者が聞き、話し方に対する聴覚印象によって「はっきり」と「会話調」とに音声を分類した場合、「はっきり」に分類された音声の正解率の方が高かった。
今後の検討
私たちの研究を通じて、高齢者・聴覚障害者・非母語話者のための音声のバリアフリーの実現や、より高性能な補聴器の設計(例:小林ら, 2008)などに貢献するものと期待される。
デモ音声(近日公開)
- S. Furui, “On the role of spectral transition for speech perception.” J. Acoust. Soc. Am., 80(4), 1016-1025, 1986.
- T. Houtgast and H. J. M. Steeneken, “A review of MTF concept in room acoustics and its use for estimating speech intelligibility in auditoria.” J. Acoust. Soc. Am., 77(3), 1069-1077, 1985.
- A. K. Nabelek, T. R. Letowski and F. M. Tucker, “Reverberant overlap- and self-masking in consonant identification.” J. Acoust. Soc. Am., 86(4), 1259-1265, 1989.
- T. Arai, K. Kinoshita, N. Hodoshima, A. Kusumoto and T. Kitamura, “Effects of suppressing steady-state portions of speech on intelligibility in reverberant environments,” Proc. Autumn Meet. Acoust. Soc. Jpn., 1, 449-450, 2001 (in Japanese).
- T. Arai, K. Kinoshita, N. Hodoshima, A. Kusumoto and T. Kitamura, “Effects of suppressing steady-state portions of speech on intelligibility in reverberant environments,” Acoust. Sci. Tech., 23(4), 229-232, 2002.
- T. Arai, K. Yasu and N. Hodoshima, “Effective speech processing for various impaired listeners,” Proc. International Congress on Acoustics, II, 1389-1392, 2004 (Invited Paper).
- T. Arai, “Padding zero into steady-state portions of speech as a preprocess for improving intelligibility in reverberant environments,” Acoust. Sci. Tech., 25(5), 459-461, 2005.
- T. Arai and N. Hodoshima, “Temporally enhanced speech is more intelligible in reverberant environments,” Proc. WESPAC, 2006 (Invited Paper).
- T. Arai, “Preprocessing speech against reverberation,” J. Acoust. Soc. Am., 120(5), 3323, 2006 (Invited Paper).
- T. Arai, Y. Nakata, N. Hodoshima and K. Kurisu, “Decreasing speaking-rate with steady-state suppression to improve speech intelligibility in reverberant environments,” Acoust. Sci. Tech., 28(4), 282-285, 2007.
- T. Arai, Y. Murakami, N. Hayashi, N. Hodoshima and K. Kurisu, “Inverse correlation of intelligibility of speech in reverberation with the amount of overlap-masking,” Acoust. Sci. Tech., 28(6), 438-441, 2007.
- N. Hayashi, T. Arai, N. Hodoshima, Y. Miyauchi and K. Kurisu, “Steady-state pre-processing for improving speech intelligibility in reverberant environments: Evaluation in a hall with an electrical reverberator,” Proc. Interspeech, 1741-1744, 2005.
- N. Hayashi, N. Hodoshima, T. Arai and K. Kurisu, “Influence of Deutlichkeit value and reverberation time on improved speech intelligibility in reverberant environments because of steady-state suppression,” J. Acoust. Soc. Am., 120(5), 3360, 2006.
- N. Hodoshima, T. Arai and A. Kusumoto, “Enhancing temporal dynamics of speech to improve intelligibility in reverberant environments,” Proc. Forum Acusticum, 2002.
- N. Hodoshima, T. Inoue, T. Arai and A. Kusumoto, “Suppressing steady-state portions of speech for improving intelligibility in various reverberant environments,” Proc. China-Japan Joint Conference on Acoustics, 199-202, 2002.
- N. Hodoshima, T. Arai, T. Inoue, K. Kinoshita and A. Kusumoto, “Improving speech intelligibility by steady-state suppression as pre-processing in small to medium sized halls,” Proc. Eurospeech, 1365-1368, 2003.
- N. Hodoshima, T. Arai, T. Inoue, K. Kinoshita and A. Kusumoto, “Improving intelligibility of speech by steady-state suppression as pre-processing in small to medium sized halls,” International Workshop on Speech Dynamics by Ear, Eye, Mouth and Machine, Technical Report of IEICE Japan, SP2003-53, 61-66, 2003.
- N. Hodoshima, T. Inoue, T. Arai, A. Kusumoto and K. Kinoshita, “Suppressing steady-state portions of speech for improving intelligibility in various reverberant environments,” Acoust. Sci. Tech., 25(1), 58-60, 2004.
- N. Hodoshima, T. Goto, N. Ohata, T. Inoue and T. Arai, “The effect of pre-processing for improving speech intelligibility in the Sophia University lecture hall,” Proc. International Congress on Acoustics, III, 2389-2392, 2004.
- N. Hodoshima, T. Goto, N. Ohata, T. Inoue and T. Arai, “The effect of pre-processing approach for improving speech intelligibility in a hall: Comparison between diotic and dichotic listening conditions,” Acoust. Sci. Tech., 26(2), 212-214, 2005.
- N. Hodoshima, T. Arai, A. Kusumoto and K. Kinoshita, “Improving syllable identification by a preprocessing method reducing overlap-masking in reverberant environments,” J. Acoust. Soc. Am., 119(6), 4055-4064, 2006.
- N. Hodoshima and T. Arai, “Investigating an optimum suppression rate of steady-state portions of speech that improves intelligibility the most as a pre-processing approach in reverberant environments,” J. Acoust. Soc. Am., 118(3), 1930, 2005.
- N. Hodoshima, D. Behne and T. Arai, “Steady-state suppression in reverberation: A comparison of native and nonnative speech perception,” Proc. Interspeech, 873-876, 2006.
- N. Hodoshima, T. Arai and P. Svensson, “The effect of a preprocessing approach improving speech intelligibility in reverberation considering a public-address system and room acoustics,” J. Acoust. Soc. Am., 120(5), 3359, 2006.
- N. Hodoshima, D. Behne and T. Arai, “The effect of the steady-state suppression on consonant identification by native and non-native listeners in reverberant environments,” International Workshop on Frontiers in Speech and Hearing Research, Technical Report of IEICE Japan, SP2005-165, 15-20, 2006.
- N. Hodoshima and T. Arai, “Effect of talker variability on speech perception by elderly people in reverberation” in the Handbook of Auditory signal processing in hearing-impaired listeners. International Symposium on Auditory and Audiological Research, edited by T. Dau, J. M. Buchholz, J. M. Harte and T. U. Christiansen (Centertryk A/S, Holbaek), 383-387, 2007.
- N. Hodoshima, Y. Miyauchi, K. Yasu and T. Arai, “Steady-state suppression for improving syllable identification in reverberant environments: A case study in an elderly person,” Acoust. Sci. Tech., 28(1), 53-55, 2007.
- N. Hodoshima, P. Svensson and T. Arai, “Preprocessing effects on speech intelligibility in reverberation using mixed natural and electroacoustical sounds,” Proc. Japan-China Joint Conference of Acoustics, 2007.
- N. Hodoshima, T. Arai and K. Kurisu, “Effects of training, style, and rate of speaking on speech perception of young people in reverberation,” Acoustics 08 Paris, 2393-2397, 2008.
- N. Hodoshima, W. Yoshida and T. Arai, “Improving consonant identification in noise and reverberation by steady-state suppression as a preprocessing approach,” Proc. Interspeech, 1793-1796, 2008.
- T. Goto, T. Inoue, N. Ohata, N. Hodoshima and T. Arai, “The effect of pre-processing for improving speech intelligibility in the Sophia University lecture hall,” Proc. Autumn Meet. Acoust. Soc. Jpn., 1, 613-614, 2003 (in Japanese, Poster Award).
- T. Kitamura, K. Kinoshita, T. Arai, A. Kusumoto and Y. Murahara, “Designing modulation filters for improving speech intelligibility in reverberant environments,” Proc. ICSLP, 3, 586-589, 2000.
- K. Kobayashi, Y. Hatta, K. Yasu, S. Minamihata, N. Hodoshima, T. Arai and M. Shindo, “Improving speech intelligibility for elderly listeners by steady-state suppression,” International Workshop on Frontiers in Speech and Hearing Research, Technical Report of IEICE Japan, SP2005-168, 31-36, 2006.
- K. Kobayashi, K. Yasu, N. Hodoshima, T. Arai and M. Shindo, “A study of syllable enhancement for elderly listeners by suppressing energy of steady-state portions of vowels,” J. Acoust. Soc. Jp, 64(5), 278-289, 2008 (in Japanese).
- A. Kusumoto, T. Arai, T. Kitamura, M. Takahashi and Y. Murahara, “Speech processing on the room acoustics for the hearing-impaired,” Proc. Autumn Meet. Acoust. Soc. Jpn., 1, 389-390, 1999 (in Japanese).
- A. Kusumoto, T. Arai, T. Kitamura, M. Takahashi and Y. Murahara, “Modulation enhancement of speech as a preprocessing for reverberant chambers with the hearing-impaired,” Proc. IEEE ICASSP, 2, 853-856, 2000.
- A. Kusumoto, T. Arai, K. Kinoshita, N. Hodoshima and N. Vaughan, “Modulation enhancement of speech by a pre-processing algorithm for improving intelligibility in reverberant environments,” Speech Communication, 45(2), 101-113, 2005.
- Y. Miyauchi, N. Hodoshima, K. Yasu, N. Hayashi, T. Arai and M. Shindo, “A preprocessing technique for improving speech intelligibility in reverberant environments: The effect of steady-state suppression on elderly people,” Proc. Interspeech, 2769-2772, 2005.
- Y. Miyauchi and T. Arai, “Energy suppression of steady-state portions of vowels while maintaining the energy of consonants better improves speech intelligibility for elderly listeners in reverberation,” J. Acoust. Soc. Am., 120(5), 3346-3347, 2006.
- Y. Nakata, Y. Murakami, N. Hodoshima and T. Arai, “Slowed speech spreading into reverberant environments; steady-state suppression improves speech intelligibility,” J. Acoust. Soc. Am., 120(5), 3360, 2006.
- Y. Nakata, Y. Murakami, N. Hodoshima, N. Hayashi, Y. Miyauchi, T. Arai and K. Kurisu, “The effects of speech-rate slowing for improving speech intelligibility in reverberant environments,” International Workshop on Frontiers in Speech and Hearing Research, Technical Report of IEICE Japan, SP2005-166, 21-24, 2006.
- K. Takahashi, K. Yasu, N. Hodoshima, T. Arai and K. Kurisu, “Enhancing speech in reverberation by steady-state suppression,” Proc. International Congress on Acoustics, 2007.